The Rarest and Most Unusual Flowers on Earth: A Photo Gallery

The Fascinating World of Rare and Unusual Flowers
FAQ
-
What are rare and unusual flowers?
A: Rare and unusual flowers refer to a diverse group of plant species that possess unique characteristics, distinct adaptations, or captivating appearances. These flowers often stand out from more common blooms due to their rarity, unusual shapes, colours, or fragrance, and the extraordinary features that make them captivating to behold.
-
Where can I find rare and unusual flowers?
A: Rare and unusual flowers are typically found in specific regions or habitats that suit their specific growth requirements. Some may be endemic to certain countries or even restricted to small areas within a particular ecosystem. Botanical gardens, conservatories, and specialist nurseries often cultivate and display these flowers, providing opportunities for enthusiasts and the general public to witness their beauty.
-
Are rare and unusual flowers difficult to grow?
A: Some rare and unusual flowers can be challenging to cultivate due to their specific environmental requirements or unique growth patterns. They may demand specific temperature, humidity, light conditions, or soil compositions. Additionally, some species have strict dormancy periods or irregular blooming cycles, making them more complex to grow successfully. However, with proper research, understanding, and appropriate care, it is possible to cultivate many of these unique flowers.
-
Are rare and unusual flowers endangered?
A: Yes, many rare and unusual flowers are endangered or threatened due to various factors, including habitat destruction, climate change, illegal harvesting, and invasive species. The rarity and desirability of these flowers can make them targets for collectors and traders, putting further pressure on their populations. Conservation efforts, such as habitat preservation, cultivation in botanical gardens, and strict regulations on collecting, aim to protect these species and ensure their survival.
-
Do rare and unusual flowers have any cultural significance?
A: Yes, rare and unusual flowers often hold cultural significance in different societies and traditions. They may be featured in folklore, literature, and art, symbolising various emotions, virtues, or cultural beliefs. Some flowers are associated with religious or spiritual practices, while others are valued for their medicinal properties in traditional healing systems. Their unique qualities make them subjects of fascination and inspiration across different cultures.
-
Can I grow rare and unusual flowers in my garden?
A: Depending on the specific flower and your local climate, it may be possible to grow certain rare and unusual flowers in your garden. It is essential to research the specific requirements of the flower, such as light, temperature, humidity, and soil conditions. Additionally, consider the feasibility of replicating the flower's natural habitat and the availability of seeds or plants from reputable sources. Consulting with local gardening experts or horticulturists can provide valuable guidance for successful cultivation.
-
Can rare and unusual flowers be harmful or toxic?
A: While most rare and unusual flowers are not harmful or toxic, it is crucial to exercise caution and handle them with care. Some flowers may have sap, thorns, or hairs that can cause irritation or allergic reactions. It is advisable to research the specific flower's potential hazards and follow proper handling instructions. If in doubt, consult reputable sources or seek advice from horticultural experts to ensure your safety when dealing with these unique blooms.
-
How can I contribute to the conservation of rare and unusual flowers?
A: There are several ways you can contribute to the conservation of rare and unusual flowers. Supporting botanical gardens and conservation organisations dedicated to preserving endangered plant species is one impactful approach. Avoiding the illegal trade of rare flowers and seeds, respecting natural habitats, and promoting sustainable gardening practices are other ways to contribute. By raising awareness and sharing knowledge about these flowers, you can also inspire others to appreciate and protect these remarkable blooms.
-
Can I purchase rare and unusual flowers?
A: It may be possible to purchase certain rare and unusual flowers from specialist nurseries or reputable online retailers. However, it is crucial to ensure that the sources adhere to ethical and sustainable practices, do not support illegal trade or collection from the wild, and provide proper documentation and information about the origin of the plants. Always research the reputation and reliability of sellers before making any purchases.
-
Can rare and unusual flowers be grown indoors?
A: Some rare and unusual flowers can be successfully grown indoors, depending on their specific requirements. Factors such as lighting conditions, temperature, humidity levels, and space availability play crucial roles in indoor cultivation. It is essential to research the flower's specific needs and provide suitable growing conditions, including proper ventilation, appropriate containers, and regular monitoring. Some rare flowers, however, may require outdoor conditions or larger spaces to thrive optimally.
The sheer diversity of plant life on our planet is nothing short of awe-inspiring. There are over 390,000 known species of plants, and among them, flowers hold a place of unique fascination and admiration. From the commonplace roses and sunflowers to the exotic orchids and lilies, flowers have been a source of inspiration, symbolism, and intrigue throughout human history. But today, we are setting out on a journey to explore those blooms that aren't found in every garden or bouquet. We are heading into the fascinating world of rare and unusual flowers - those that charm us with their oddities, their unique characteristics, and sometimes, their strange beauty.
The Corpse Flower: A Titan Among Blooms

In the botanical world, few flowers command attention and curiosity like the Corpse Flower. Scientifically known as Amorphophallus titanum, this extraordinary plant earns its name from the pungent odour it emits when in bloom, reminiscent of rotting flesh. With its colossal size, remarkable inflorescence, and unusual olfactory attributes, the Corpse Flower stands as a titan among blooms, capturing the imagination of all who encounter it.
The Corpse Flower is native to the rainforests of Sumatra, Indonesia, where it thrives in the warm and humid conditions of its natural habitat. It is renowned for producing one of the largest inflorescences in the plant kingdom, reaching heights of up to three metres. This remarkable structure consists of a central spadix surrounded by a frilly, leaf-like structure known as the spathe, which can take on varying shades of deep maroon or green.
What sets the Corpse Flower apart is not only its grand stature but also its infrequent and dramatic blooming cycle. The plant remains dormant for several years, often growing as a single leafy stalk during this period. Then, seemingly out of nowhere, it produces the awe-inspiring inflorescence, with the spathe unfurling to reveal the spadix at its centre.
But perhaps the most infamous attribute of the Corpse Flower is its intense and peculiar aroma. When the flower is in bloom, it emits a foul stench reminiscent of rotting meat. This odour serves a vital purpose in nature—it attracts carrion beetles and flies, which mistake the flower for a decaying animal and become lured into its trap. As the insects crawl inside the spathe in search of a meal, they inadvertently come into contact with the plant's male and female reproductive structures, aiding in the process of pollination.
The Corpse Flower's blooming event is a spectacle that captivates and astounds. People from around the world flock to botanical gardens and greenhouses when news of a blooming Corpse Flower spreads. The rarity and infrequent nature of its blooming cycle add to the allure, making it a true botanical marvel that leaves a lasting impression on those fortunate enough to witness it.
Despite its reputation as a flower with a repugnant odour, the Corpse Flower plays a crucial role in its ecosystem. It contributes to the diversity and health of its rainforest habitat by providing a food source for certain pollinators and facilitating the cross-pollination of other plants. It is a reminder that even in the world of putrid scents, there can exist beauty and purpose.
The Corpse Flower's unique attributes and grandeur have sparked fascination and scientific inquiry. Researchers continue to study its biology, seeking to unravel the mysteries behind its incredible growth patterns, its remarkable scent production, and the mechanisms that drive its infrequent blooming events. By understanding the intricacies of the Corpse Flower, scientists hope to gain insights into broader botanical and ecological questions.
In the presence of the Corpse Flower, one is simultaneously captivated and repelled by its extraordinary size, striking appearance, and distinct aroma. It serves as a reminder of the diversity and ingenuity of the natural world, showcasing nature's ability to create awe-inspiring wonders that challenge our perceptions and ignite our sense of wonder. The Corpse Flower truly stands as a titan among blooms, both captivating and evocative, and forever etching its unique presence in our botanical consciousness.
The Monkey Face Orchid: A Primate in Petals

In the enchanting world of orchids, one flower stands out as a true mimic of the animal kingdom—the Monkey Face Orchid. Known scientifically as Dracula simia, this extraordinary orchid captivates the imagination with its uncanny resemblance to a primate's face. Its intricate floral structure and charming allure make it a botanical marvel that delights both nature enthusiasts and curious observers.
The Monkey Face Orchid is native to the cloud forests of Ecuador and Peru, where it thrives in the cool, misty climates of the high-altitude regions. What sets this orchid apart from others is its remarkable floral adaptation, which resembles the face of a monkey in astonishing detail. From the large, round "eyes" to the intricate "nose" and "mouth," every feature is meticulously crafted by nature to imitate the expressions of these playful creatures.
The flower of the Monkey Face Orchid emerges from the stem, presenting a single blossom that captures the essence of a primate's face. Its petals and sepals are carefully arranged to create the illusion of fur, with intricate patterns and colouration that mimic the textures found on the skin of a primate. The varying shades of brown, beige, and green add to the authenticity of the resemblance, as if the flower is wearing a primate mask.
The Monkey Face Orchid's unique floral adaptation serves a purpose beyond mere aesthetics. The intricate features and colour patterns are believed to play a role in attracting pollinators. It is thought that certain species of bees and insects, particularly those that have coevolved with the orchid, are drawn to the flower by the resemblance to a primate's face. As they explore the flower in search of nectar, they inadvertently aid in pollination by carrying pollen from one flower to another.
The captivating charm of the Monkey Face Orchid has made it a sought-after treasure for orchid enthusiasts and collectors. Its distinctiveness and rarity have garnered attention worldwide, making it a subject of admiration and intrigue. However, the plant's popularity and habitat destruction have also put it at risk, underscoring the importance of conservation efforts to protect this remarkable botanical wonder.
The Monkey Face Orchid serves as a reminder of the astonishing diversity and ingenuity found in the natural world. Its mimicry of a primate's face is a testament to the wonders of evolution, showcasing nature's ability to create intricate adaptations that captivate and astound. This extraordinary orchid invites us to appreciate the playful and imaginative qualities of the natural world.
In the presence of the Monkey Face Orchid, one cannot help but be drawn into its charm and marvel at the primate-like visage it presents. It serves as a whimsical reminder of the interconnectedness of all living beings and the boundless creativity that exists in the floral realm. The Monkey Face Orchid truly embodies the magic of nature, transforming petals into a primate, and enchanting all who are fortunate enough to witness its presence.
The Ghost Orchid: An Ethereal Beauty
In the mysterious realm of orchids, there exists a flower of such exquisite beauty and elusive nature that it has earned the name "Ghost Orchid." This enigmatic plant, scientifically known as Dendrophylax lindenii, is renowned for its delicate appearance, rare sightings, and captivating allure that evokes a sense of ethereal enchantment.
The Ghost Orchid is native to the lush and humid swamplands of Florida, Cuba, and the Bahamas. It is an epiphytic orchid, meaning it grows attached to trees or other plants, drawing its nutrients and moisture from the air and rain. What sets this orchid apart from others is its remarkable strategy for survival, which involves blending seamlessly with its surroundings and making itself nearly invisible.
At first glance, the Ghost Orchid may seem like an apparition, with its translucent, waxy petals and elongated tendrils that give it an otherworldly appearance. The flower lacks leaves and typically features one or two white blooms that appear to float in mid-air, seemingly untouched by the physical world. The petals are often described as ghostly due to their pale colouration and delicate, almost ethereal texture.

But what truly adds to the mystique of the Ghost Orchid is its elusiveness. The plant is notoriously challenging to spot and study in the wild, making sightings a rare and treasured experience. It has a peculiar habit of blooming irregularly, with some individuals flowering only once every few years, and others even less frequently. This irregularity, combined with its preference for remote and inaccessible habitats, makes encountering a blooming Ghost Orchid a moment of profound wonder.
Another intriguing aspect of the Ghost Orchid is its pollination strategy. In the absence of obvious nectar rewards, it relies on specific species of nocturnal moths for pollination. These moths are attracted to the orchid's subtle fragrance, which they can detect even in the darkness of the night. As the moths navigate the flower, they inadvertently come into contact with the orchid's pollen, facilitating cross-pollination and the perpetuation of the species.
The rarity and allure of the Ghost Orchid have made it the subject of fascination and intrigue for both botanists and nature enthusiasts. Scientists have dedicated years to understanding its ecological niche, reproductive biology, and conservation needs. Efforts to protect and preserve the Ghost Orchid and its delicate habitat are essential, as it faces threats such as habitat destruction and illegal collecting.
The Ghost Orchid's delicate beauty, combined with its mysterious nature and rare sightings, exemplify the extraordinary diversity and complexity of the natural world. It serves as a reminder that even in the hidden corners of our planet, there exist breathtaking treasures waiting to be discovered. The Ghost Orchid invites us to embrace the wonder and magic of the natural world, encouraging us to protect and cherish these ethereal beauties for generations to come.
In the realms of imagination and botanical fascination, the Ghost Orchid stands as a symbol of ethereal beauty, a reminder of the delicate balance between rarity and preservation that defines the enchantment of our natural world.
The Parrot's Beak: A Dazzling Display
In the realm of vibrant and exotic blooms, few flowers command attention quite like the Parrot's Beak. This captivating flower, scientifically known as Lotus berthelotii, showcases a dazzling display of vibrant colours and unique structural elements that resemble the beak of a parrot. Its striking appearance and extraordinary adaptations make it a true marvel of the botanical world.
The Parrot's Beak is a perennial plant native to the Canary Islands, where it thrives in the rocky, volcanic terrains of its natural habitat. The flower's distinctive shape is reminiscent of a parrot's beak, with its curved, slender petals that form a tubular structure. The vibrant hues of red, orange, and yellow adorn the petals, adding to the flower's enchanting allure.
One of the most remarkable aspects of the Parrot's Beak is its adaptation for pollination. The tubular shape of the flower and its bright, contrasting colours are specifically designed to attract certain bird species, particularly sunbirds and hummingbirds. These avian pollinators, with their long, slender beaks and ability to hover in mid-air, are perfectly suited to reach deep into the flower's tube and access its nectar reserves.

As the birds feed on the nectar, they inadvertently come into contact with the flower's reproductive structures, facilitating the transfer of pollen from one flower to another. This intricate relationship between the Parrot's Beak and its avian pollinators is a prime example of coevolution, where both the flower and the bird have adapted in response to each other over time.
Beyond its remarkable pollination strategy, the Parrot's Beak possesses other adaptations that allow it to thrive in its unique environment. The plant has succulent-like leaves that help it retain moisture, enabling it to withstand the arid conditions of its native habitat. It also has a sprawling growth habit, with trailing stems that cascade over rocks and walls, creating a captivating visual display.
The Parrot's Beak's ability to add a touch of exotic splendour to gardens and landscapes has made it a sought-after plant among horticultural enthusiasts. Its vibrant colours and unique floral structure make it a prized addition to floral arrangements, adding a sense of tropical allure and beauty.
In addition to its aesthetic appeal, the Parrot's Beak holds cultural significance in the Canary Islands. It is often associated with the vibrant traditions and rich biodiversity of the archipelago. In local folklore, the flower is considered a symbol of resilience and adaptability, as it thrives in challenging environments, much like the people of the Canary Islands themselves.
The Parrot's Beak's dazzling display serves as a testament to the remarkable beauty and diversity of the natural world. Its vivid colours, intricate adaptations, and coevolutionary relationships highlight the wonders of evolution and the delicate balance of ecosystems. This captivating flower reminds us of the importance of preserving and appreciating the biodiversity that surrounds us.
With its vibrant hues and distinctive form, the Parrot's Beak stands as a testament to the mesmerising beauty and remarkable adaptations found in the plant kingdom. Its dazzling display captures our imagination, reminding us of the extraordinary wonders that nature has to offer.
The Bleeding Heart: A Tearful Elegance
In the enchanting world of flowers, few capture the imagination quite like the Bleeding Heart. With its delicate form and poignant symbolism, this captivating flower, scientifically known as Dicentra spectabilis, evokes a sense of elegance and melancholic beauty.
The Bleeding Heart is native to eastern Asia and is a herbaceous perennial that thrives in cool, moist conditions. When it comes into bloom, usually in late spring or early summer, it presents a breathtaking display of tear-shaped flowers that dangle gracefully from arching stems. These flowers, typically pink or white, bear a striking resemblance to tiny, upside-down hearts, which gives rise to its evocative name.
One cannot help but be captivated by the Bleeding Heart's distinctive floral structure. Each blossom consists of two outer petals that form a protective arch around the inner petals. These inner petals, which are usually a deeper shade of pink, combine to create the iconic heart shape. The striking contrast between the delicate, pale outer petals and the vibrant, heart-like inner petals adds to the flower's visual allure.
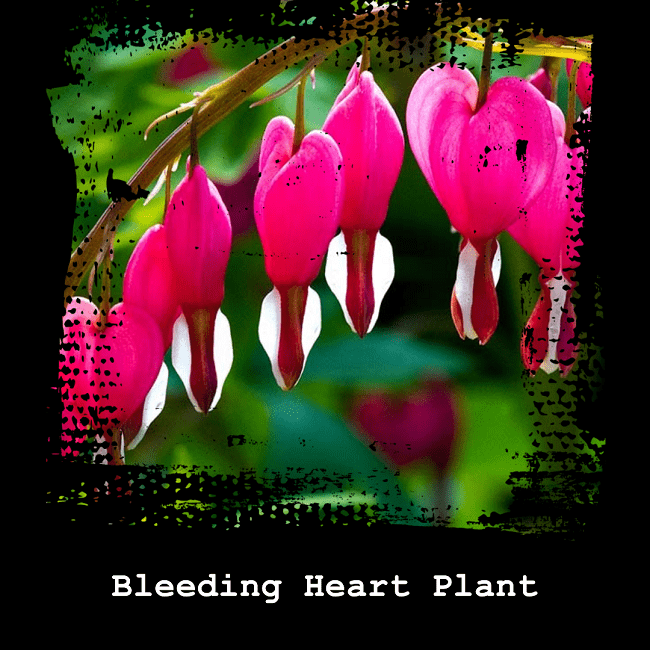
What truly sets the Bleeding Heart apart is its tear-shaped pendant, or "drop". Positioned at the base of the heart-shaped petals, this droplet-like structure gives the flower an element of emotional depth. It appears as if the Bleeding Heart is shedding a tear, conveying a sense of tender vulnerability and emotional expression.
Beyond its enchanting appearance, the Bleeding Heart carries symbolic meanings that have captivated hearts throughout history. It is often associated with themes of love, compassion, and deep emotions. The flower's tear-shaped droplet has been interpreted as a symbol of a broken heart or a love that yearns and laments. This rich symbolism has made the Bleeding Heart a popular choice in gardens and floral arrangements, particularly for those seeking to convey sentiments of love and emotional depth.
Culturally, the Bleeding Heart holds significance in various traditions. In some cultures, the flower is associated with the Virgin Mary and is considered a symbol of purity and grace. In others, it is believed to possess healing properties and is used in traditional herbal medicine to address ailments of the heart, both physical and emotional.
The Bleeding Heart's ephemeral nature adds to its charm. While it may only grace our gardens for a relatively short period each year, its brief appearance is eagerly anticipated and cherished. Its transient beauty serves as a reminder to appreciate the fleeting moments of life and the delicate nature of our own emotions.
Whether adorning a garden, featured in an arrangement, or celebrated in art and literature, the Bleeding Heart stands as a timeless symbol of tearful elegance and heartfelt emotion. It invites us to reflect on the depths of our own feelings and the importance of embracing the fleeting beauty that surrounds us.
In the presence of the Bleeding Heart, one can't help but be moved by its delicate petals and its tearful elegance, reminding us of the intricate and tender aspects of our own hearts.
Welwitschia Mirabilis: The Ancient Endurance
In the desolate landscapes of the Namib Desert in southwestern Africa, a living testament to resilience and endurance stands proud - the Welwitschia mirabilis. This fascinating plant is often regarded as a living fossil, representing a lineage that dates back millions of years, and its ability to survive in such harsh conditions is nothing short of extraordinary.
The Welwitschia mirabilis is a gymnosperm, a type of plant that produces seeds without the use of flowers. Its growth form is unique and unmistakable - it consists of just two long, strap-like leaves that emerge from a woody base near ground level. These leaves grow continuously throughout the plant's lifespan, which can span several centuries. Over time, the leaves become frayed and split into several lobes, giving them a distinct appearance reminiscent of tattered fabric.

The Welwitschia mirabilis is a master of adaptation to its arid environment. It has evolved several remarkable features that enable it to thrive in the harsh desert conditions. One of its most notable adaptations is its ability to absorb moisture from the dense coastal fog that blankets the Namib Desert. The plant has specialized structures on its leaves that capture and channel moisture towards its base, allowing it to survive in an environment where water is scarce.
Another fascinating characteristic of the Welwitschia mirabilis is its incredibly long lifespan. Some individuals are estimated to be over 2,000 years old, making them among the oldest living plants on Earth. These ancient individuals have witnessed the passage of time, persevering through countless droughts, sandstorms, and other challenges that come with surviving in an unforgiving desert.
The Welwitschia mirabilis is a true marvel of endurance. Despite its slow growth rate, limited leaf count, and minimalistic appearance, it has adapted to its environment in ways that have allowed it to persist for millennia. Its ability to extract water from fog and survive on minimal resources is a testament to its resilience and ability to withstand extreme conditions.
This plant's significance goes beyond its botanical features. It holds cultural and ecological value for the people and ecosystems of the Namib Desert. Indigenous communities have long revered the Welwitschia mirabilis for its ability to survive in the harshest of environments, considering it a symbol of strength and resilience.
From a scientific perspective, the Welwitschia mirabilis is a fascinating subject of study. Researchers continue to unravel its secrets, examining its unique adaptations, the genetic basis of its longevity, and its intricate relationship with its environment. By understanding the mechanisms behind its endurance, scientists hope to glean insights that can aid in the conservation of other vulnerable species and help us adapt to our changing planet.
The Welwitschia mirabilis stands as a living testament to the ancient endurance of life on Earth. It serves as a reminder that in the face of adversity, remarkable adaptations and resilience can emerge. This incredible plant inspires awe and admiration, reminding us of the wonders of nature and the astonishing abilities of organisms to survive and flourish in the most challenging of circumstances.
Rafflesia arnoldii: The Enormous Bloom
If one thinks about 'large flowers', the mind might conjure up sunflowers or perhaps even the giant water lily. But these all pale in comparison to the Rafflesia arnoldii, often called the 'corpse flower'. Native to the rainforests of Indonesia, Rafflesia arnoldii holds the record for producing the world's largest individual flower, and it is a botanical marvel that astounds with its sheer size and peculiar characteristics.
The most striking aspect of Rafflesia arnoldii is, of course, its bloom. The flower can grow to a staggering diameter of one metre and can weigh up to 11 kilograms – a true titan of the botanical world. But the most astounding feature is perhaps its parasitic lifestyle. The plant lacks leaves, stems, or roots. Instead, it lives inside its host, the Tetrastigma vine, sapping nutrients and only emerging to reveal its enormous, fleshy, five-petalled flower. It's an extreme example of adaptation to a parasitic lifestyle.

Each petal of Rafflesia arnoldii is thick and leathery, speckled with white freckles. The centre of the flower contains a deep well that houses a central disk and numerous spiky structures. The flower's anatomy is as remarkable as its size. But as alluring as its appearance might be, its smell is quite the opposite.
The Rafflesia arnoldii is often referred to as the 'corpse flower' because of the smell it produces to attract pollinators. It emits a strong, foul odour similar to rotting flesh, and it's this smell that attracts carrion flies. These insects normally lay their eggs on decaying meat, but the scent of Rafflesia arnoldii tricks them. When they arrive, looking for a place to lay their eggs, they instead pick up pollen from the flower and transfer it to the next bloom they visit.
However, this elaborate reproductive strategy has its drawbacks. As the plant is entirely dependent on its host for nutrients, it can only grow in certain areas where the vine is present. Additionally, the reliance on carrion flies for pollination, coupled with the flower's relatively short lifespan of just a few days, makes successful fertilisation a rare event.
The Rafflesia arnoldii is a true wonder of the natural world, demonstrating the lengths to which evolution can go in the name of survival. Despite its seemingly alien characteristics and its rather unflattering nickname, the 'corpse flower' stands as a testament to the incredible diversity and adaptability of life on our planet.
In the current climate of rapid deforestation and habitat loss, the Rafflesia arnoldii, like many other unique and unusual flowers, is at risk. It serves as a stark reminder of the need for ongoing conservation efforts to preserve the world's biodiversity, no matter how unusual or unorthodox it may seem.
The Naked Man Orchid: The Hilarious Mimicry
The Orchis italica, commonly known as the Naked Man Orchid or the Italian Orchid, is a flower that causes much mirth due to its peculiar appearance. This unusual flower, native to the Mediterranean regions, is well-known for the curious shape of its blooms which amusingly resemble tiny, naked men.
This delightful perennial blooms in the early spring, typically from April to May, with the flowers forming dense clusters along the inflorescence. Each flower is small, typically no more than a centimetre across, and is marked by an uncanny resemblance to a tiny humanoid figure. The "body" or labellum of the flower, typically pink or purplish in colour, has two "arms" and "legs" that extend from a central "torso". Above this body sits a hood or "head", completing the form.

What makes this botanical mimicry even more impressive is the detail within each flower. The lobes that form the legs often bear markings that resemble minute shoes or boots, and there are occasionally even markings on the body of the flower that give the illusion of facial features or decorative adornment. This intricate mimicry is not just a quirk of evolution but serves a vital purpose for the survival of the Orchis italica.
The whimsical appearance of the Naked Man Orchid serves to attract pollinators. In this case, the pollinators are primarily bees. The flower emits a scent that draws in these pollinators, and the intriguing shape of the bloom encourages the insects to linger, promoting cross-pollination between flowers.
However, this form of deception is not only confined to visual mimicry. The Naked Man Orchid also emits pheromones that mimic those of female bees. This draws in male bees, who are fooled into attempting to mate with the flowers, thereby facilitating pollination.
Beyond its intriguing morphology and reproductive strategy, the Orchis italica is also notable for its resilience. This hardy plant thrives in a range of habitats, from open grasslands to shaded woodland areas and from sea level to mountainous regions. It is a testament to the plant's adaptability that it can be found across such diverse climatic zones.
The Orchis italica, with its unique shape and fascinating survival strategies, adds a touch of whimsy to the world of unusual flowers. Its ability to bring joy and laughter to those who encounter it is as noteworthy as its evolutionary adaptations. The Naked Man Orchid thus serves as a delightful example of nature's capacity for humour and charm, reminding us that even in the pursuit of survival, there can be elements of fun and playfulness.
The Hydnora Africana: A Subterranean Wonder
When it comes to the Hydnora africana, we encounter an utterly remarkable specimen that truly pushes the boundaries of our preconceived notions about what a flower should look like and how it should behave. This outlandish plant is a native of the arid regions of southern Africa, a locale that has certainly influenced its peculiar life strategies and morphology.
The Hydnora africana is essentially a parasitic plant, devoid of chlorophyll, and completely reliant on its host plant, typically a species of Euphorbia, for nutrients. A significant part of its life cycle is spent underground, latched onto the roots of its host, from which it draws sustenance.
One of the most striking characteristics of the Hydnora africana is its extraordinary flowering structure. Unlike other flowers that bloom above ground and compete for the attention of pollinators with vivid colours and enchanting fragrances, the Hydnora africana blooms below the surface of the soil. The flower emerges as a fleshy, almost alien-like structure, which is predominantly brown and bears an unsettling resemblance to a creature from a science fiction novel.
The bloom of the Hydnora Africana can take up to a year to form, mature, and finally emerge from the ground. Once it does, the flower opens up to reveal a cavernous interior, lined with bright orange spikes. But the most surprising element is yet to come - the scent. Instead of the sweet, pleasing fragrances associated with most flowers, the Hydnora Africana emits a strong, unpleasant odour akin to faeces. This unusual strategy is purposeful and cleverly adapted to its primary pollinators - beetles and other insects attracted to dung.
The pungent scent lures dung beetles and carrion beetles into the flower. Once inside, the beetles find themselves trapped by the inward-pointing spines and the flower's closing petals. However, this isn't a fatal ending for the insects. After a day or two, when the flower's female organs have been pollinated, the flower reopens, allowing the beetles to escape, covered in pollen. When these beetles enter another Hydnora Africana flower, they pollinate it, thereby ensuring the propagation of the species.
The Hydnora Africana is not just unusual in its morphology and reproductive strategy, but also in its fruiting mechanism. After pollination, the flower develops into a fruit that remains underground until it is fully ripe. The fruit, which tastes a bit like a potato, is an important source of hydration and nutrition for many animals, including humans, in the harsh, arid environments where the plant grows.
The Hydnora Africana, with its entirely underground lifestyle, deceptive pollination strategy, and strikingly odd appearance, is an extraordinary testament to nature's inventiveness and adaptability. This bizarre and fascinating plant serves as a powerful reminder of the complex and diverse strategies that life on Earth has evolved to survive and thrive.
The Pitcher Plant: A Deadly Beauty
In the world of botanical wonders, few plants captivate the imagination quite like the Pitcher Plant. This intriguing and carnivorous plant family, known scientifically as Nepenthean, includes species with various adaptations to capture and digest insects. The beauty of these plants lies not only in their mesmerizing appearance but also in their deadly allure.
Pitcher Plants are primarily found in regions with nutrient-poor soil, such as peat bogs and acidic swamps. To compensate for the lack of essential nutrients, these plants have evolved intricate mechanisms to supplement their diet by trapping and digesting unsuspecting insects.
The most distinctive feature of the Pitcher Plant is its pitcher-shaped leaves, which act as ingenious pitfalls for insects. These modified leaves form deep, tubular structures filled with a combination of nectar, digestive enzymes, and rainwater. The rim of the pitcher often bears attractive patterns or vibrant colours, enticing insects to explore further.
As curious insects venture into the pitcher, they are enticed by the irresistible aroma of nectar and the visual cues that mimic flowers or tasty treats. Slippery walls inside the pitcher make escape nearly impossible, while downward-pointing hairs further prevent insects from crawling back out. The unfortunate prey ultimately meets its demise in a pool of digestive enzymes, where it is broken down and absorbed by the plant to supplement its nutritional needs.
Pitcher Plants employ different mechanisms to attract and trap their prey. For instance, the Nepenthes rajah, found in the rainforests of Borneo, boasts colossal pitchers that can hold up to two litres of fluid. The impressive size of these traps and their reddish hues are a visual spectacle, attracting a wide range of insects, including beetles, ants, and even small mammals. Other species, like the Sarracenia purpurea of North America, feature intricate patterns, vivid colours, and alluring nectar secretions to entice insects into their deadly grasp.
The coevolutionary relationship between Pitcher Plants and their prey is a testament to the remarkable adaptability of both plants and insects. Some insects have evolved strategies to exploit the plants' nectar rewards while avoiding capture, such as perching on the pitcher's rim without entering the trap. In response, Pitcher Plants have evolved novel adaptations to deter these cunning insects and ensure successful prey capture.
While their carnivorous nature may seem ominous, Pitcher Plants serve an important ecological role in their respective habitats. By controlling insect populations, they contribute to the delicate balance of their ecosystems. Furthermore, their unusual form and captivating beauty make them a subject of fascination for researchers and nature enthusiasts alike.
The Pitcher Plant's deadly allure extends beyond its function as a predator. These remarkable plants have become a source of inspiration for artists, poets, and scientists. Their unique adaptations and coevolutionary relationships provide a window into the intricate web of life and the endless wonders of the natural world.
In a world where beauty and danger often coexist, the Pitcher Plant stands as a prime example of nature's capacity to surprise and astonish. Its deadly beauty and intricate mechanisms serve as a reminder of the incredible diversity of life on Earth, showcasing the remarkable adaptations that have allowed organisms to thrive in even the harshest of environments.
Summing Up
The world of rare and unusual flowers is a captivating realm that showcases the incredible diversity, ingenuity, and beauty of the botanical kingdom. From the enormous bloom of the Rafflesia arnoldii to the tearful elegance of the Bleeding Heart, from the ethereal beauty of the Ghost Orchid to the mimicry of the Monkey Face Orchid, and from the subterranean wonder of the Hydnora Africana to the deadly beauty of the Pitcher Plant, each flower has its own unique story to tell.
These extraordinary blooms have evolved to thrive in diverse habitats, showcasing remarkable adaptations that allow them to survive in challenging conditions. Whether it is the Rafflesia arnoldii's foul stench to attract pollinators or the Welwitschia mirabilis' ability to absorb moisture from coastal fog, each flower has found innovative ways to survive and reproduce.
Beyond their physical attributes, these flowers hold cultural significance, symbolising emotions, embodying folklore, and inspiring creativity. They remind us of the interconnectedness between nature and human culture, highlighting the deep-rooted relationship we share with the natural world.
Exploring these rare and unusual flowers also reveals the intricate relationships they have with their ecosystems. Be it the pollination partnerships between the Ghost Orchid and its avian visitors or the carnivorous nature of the Pitcher Plant, these flowers contribute to the delicate balance and biodiversity of their respective environments.
While some of these flowers are elusive and rare, their beauty and uniqueness make them subjects of admiration, study, and conservation efforts. Scientists continue to unravel their secrets, seeking to understand their biology, reproductive strategies, and ecological roles. Their research not only deepens our knowledge of these remarkable plants but also sheds light on broader questions about evolution, adaptation, and the interplay between species.
The world of rare and unusual flowers offers us a glimpse into the wonders of nature. These flowers captivate us with their striking forms, intriguing adaptations, and symbolic meanings. They invite us to appreciate the beauty and diversity that surrounds us and to recognise the importance of preserving and protecting the natural world.
As we continue to explore and learn about these extraordinary blooms, may we be inspired to cultivate a deeper connection with nature, to conserve fragile ecosystems, and to celebrate the remarkable tapestry of life that exists in our world.
Blog Categories
Recent posts
- Why Australian Natives Outlast Every Other Flower in a Gosford Office or Apartment
- What 17 Years of Orders Taught Us About Toowoomba’s Flower Tastes
- Get Well Flowers That Actually Help: - 20 Years of Stories and Advice from the Shop Floor
- The Saturday Problem: My Predictions for Valentine’s Day Flower Sales in 2026
- From Kingscliff 2007 to Now: Why June Weddings Beat the Summer Heat (and the Flowers to Prove It)
- 12 Christmas Wreath Decorating Ideas and Tips
